Discover the Crux Constellation - exciting facts, major bright stars, detailed star map, bordering constellations, name meaning, visibility, best astrophotography targets inside, and frequently asked questions. All you need to know about the constellation in one place!
Jump to:

Crux Interesting Facts
| Constellation | Crux |
| Location | Southern sky |
| Quadrant | SQ3 |
| Symbolism / English name meaning | Cross (southern), Southern Cross |
| Right ascension (RA) | 12.5h |
| Declination (DEC) | -60° |
| Best months to see (Northern hemisphere) | May (only latitudes between +20° and 0° - Hawaii/Mexico/Caribbean/North Africa/India) |
| Best months to see (Southern Hemisphere) | All year round |
| Messier objects count | 0 |
| Brightest star | α Crucis (Acrux) |
The Crux is the smallest constellation of all the 88, covering only 68 square degrees (0.165) of the night sky.
The Crux constellation was already known in ancient times. The constellation has the shape of a Latin cross. In the past, sailors used this constellation for ship navigation.
The four stars forming the Southern Cross were already known to Ptolemy, who classified them as part of the Centaurus constellation.
The symbol of the Southern Cross can be found as a part of the flag of Australia, New Zealand, Samoa, Brazil, and Papua New Guinea.
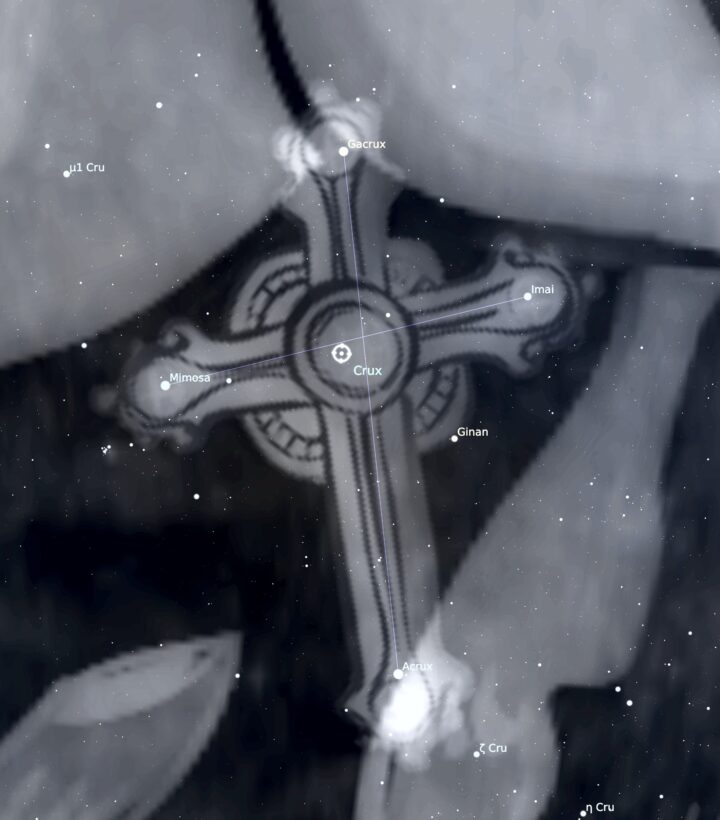
Crux Main Bright Stars
There are four major stars that form the constellation:
- α Crucis (Acrux) - the brightest star in the constellation (magnitude 0.87)
- β Crucis (Mimosa) - the second brightest star
- γ Crucis (Gacrux)
- δ Crucis (Imai)
Crux Map
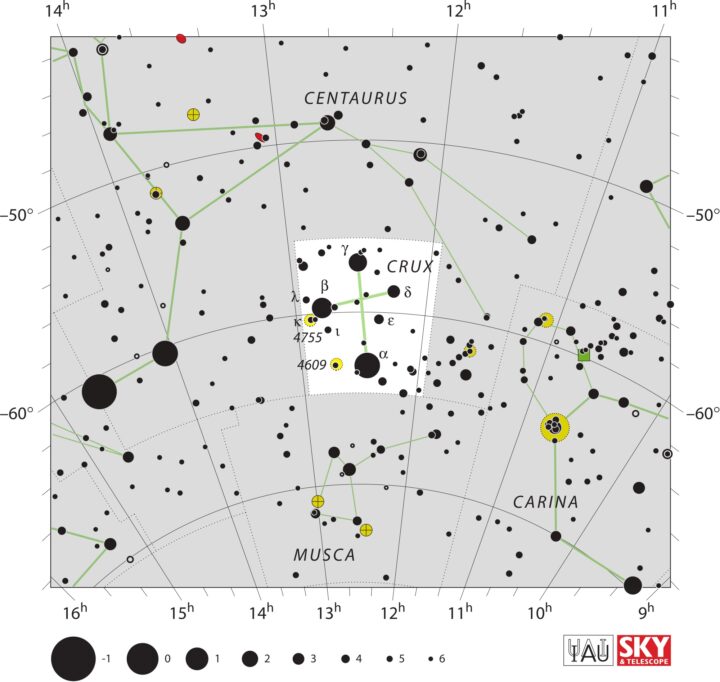
Crux Bordering Constellations
Crux Constellation borders two constellations:
- Centaurus Constellation on the east, north, and west
- Musca Constellation to the south
Interesting Deep-Sky Astrophotography Objects Inside Crux
The constellation is the home of some awesome astrophotography targets:
- Coalsack Nebula (Caldwell 99)
- Coalsack Cluster (NGC 4609)
- H05 Open Cluster
- Kappa Crucis Cluster (NGC 4755, Caldwell 94, Herschel's Jewel Box/"The Jewel Box")
FAQ
The Crux is one of the 88 official constellations, located in the southern sky, bordering Centaurus and Musca.
Amerigo Vespucci is considered to be the modern discoverer of the Southern Cross. He carried it on his maps during his expedition to South America in 1501.






Comments
No Comments